Surrogacy offers hope to individuals and couples who cannot conceive naturally, but it also raises complex legal questions—particularly concerning parental rights in surrogacy. Establishing legal parenthood is crucial to ensure that intended parents are recognized as the child’s legal guardians from birth. This article explores the legal framework surrounding parental rights in surrogacy, including key considerations, international variations, and steps to secure legal recognition.
Understanding Parental Rights in Surrogacy
Parental rights in surrogacy refer to the legal recognition of intended parents as the child’s legal guardians. Unlike traditional parenthood, where biological ties automatically establish rights, surrogacy requires legal processes to transfer parental rights from the surrogate (and possibly her spouse) to the intended parents.
There are two primary types of surrogacy:
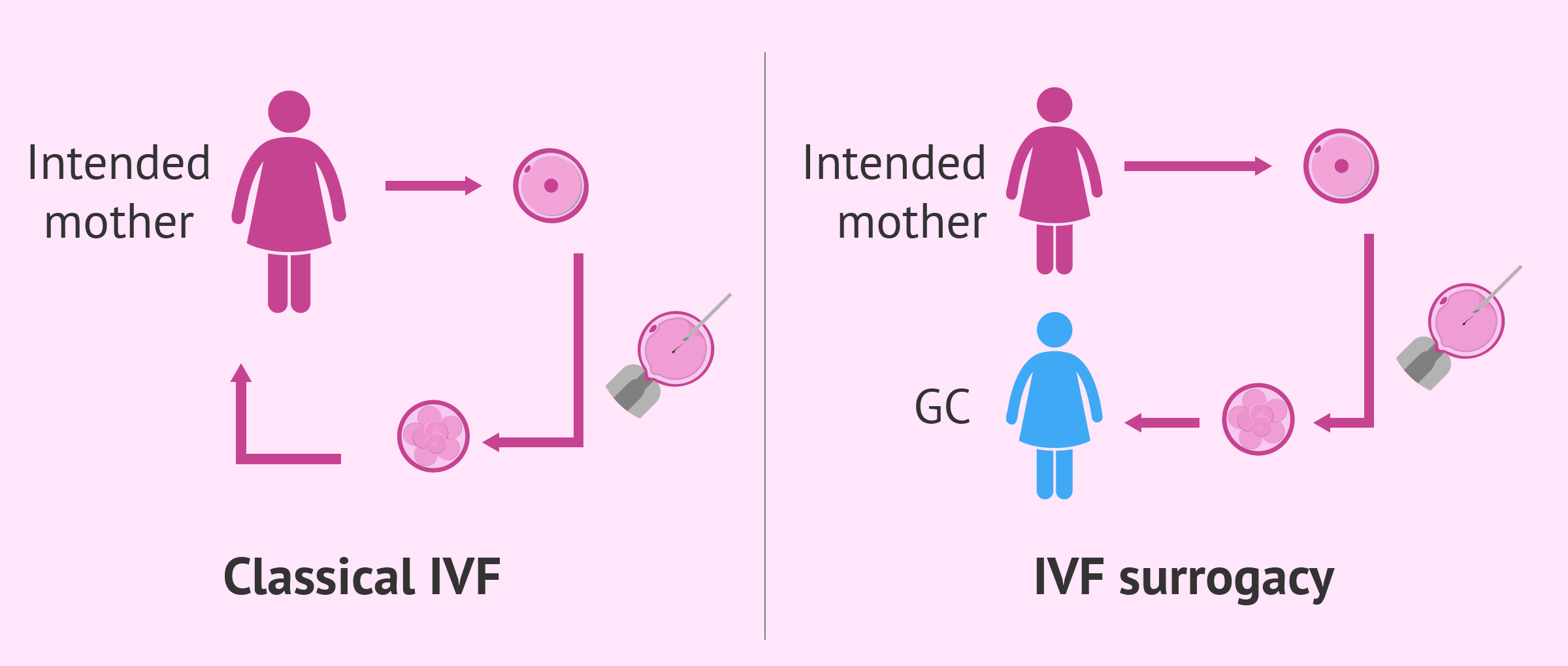
- Traditional Surrogacy – The surrogate is the biological mother of the child, as her own egg is used. This complicates parental rights in surrogacy because she has a genetic connection to the baby.
- Gestational Surrogacy – The surrogate carries an embryo created using the intended parents’ or donors’ sperm and egg, meaning she has no genetic link to the child. This is the more common and legally straightforward option.
How Parental Rights Are Established in Surrogacy
The process of securing parental rights in surrogacy varies by jurisdiction but generally involves the following steps:
Pre-Birth Orders
In some countries and U.S. states, intended parents can obtain a pre-birth order, which legally recognizes them as the child’s parents before birth. This ensures that their names appear on the birth certificate immediately.
Post-Birth Adoption or Court Orders
In regions where pre-birth orders are not available, intended parents may need to complete an adoption process or obtain a court order after birth. This can be time-consuming and may require the surrogate to relinquish her parental rights formally.
Genetic Connection Considerations
If at least one intended parent is genetically related to the child (through egg or sperm donation), courts are more likely to grant parental rights in surrogacy without requiring adoption. In cases where donors are used, legal contracts must clearly define parental rights to avoid disputes.
International Variations in Parental Rights
Laws governing parental rights in surrogacy differ significantly worldwide. Some countries fully support surrogacy, while others ban it entirely. Key jurisdictions include:
United States
The U.S. has no federal surrogacy law, meaning regulations vary by state. Some states (like California and Illinois) are surrogacy-friendly, allowing pre-birth orders. Others (like Michigan and New York until recently) impose restrictions or require post-birth adoptions.
Ukraine
Ukraine is a popular surrogacy destination due to its clear legal framework. Only married heterosexual couples can pursue surrogacy, and parental rights in surrogacy are automatically granted to the intended parents, with the surrogate having no legal claim. For more details, visit the website.
United Kingdom & Canada
These countries allow altruistic surrogacy (no commercial compensation) but require post-birth legal processes to transfer parental rights. The surrogate remains the legal mother until a court order is issued.
Countries Where Surrogacy Is Restricted
Nations like France, Germany, and Italy prohibit surrogacy, making it difficult for intended parents to secure parental rights in surrogacy even if the child is born abroad.
Legal Contracts and Parental Rights
A well-drafted surrogacy agreement is essential to protect parental rights in surrogacy. Key elements include:
- Clear identification of intended parents as the legal guardians.
- Surrogate’s consent to relinquish any parental claims.
- Compensation terms (where permitted).
- Medical and psychological screening requirements.
- Dispute resolution clauses in case of legal challenges.
Without a legally binding contract, intended parents risk lengthy court battles to establish custody.
Challenges in Establishing Parental Rights
Despite legal safeguards, disputes over parental rights in surrogacy can arise. Common issues include:
Surrogate Changing Her Mind
While rare, some surrogates may attempt to keep the child. Strong legal contracts and psychological screening minimize this risk.
Legal Recognition in Home Country
If surrogacy is conducted abroad, intended parents must ensure their home country recognizes their parental rights in surrogacy. Some nations require additional legal steps, such as re-adoption.
Same-Sex Couples and Single Parents
In some jurisdictions, only heterosexual married couples can pursue surrogacy. Same-sex couples or single parents may face additional legal hurdles in securing parental rights.
Steps to Protect Parental Rights in Surrogacy
To avoid legal complications, intended parents should:
- Choose a surrogacy-friendly jurisdiction where laws clearly support intended parents’ rights.
- Work with experienced surrogacy attorneys to draft enforceable contracts.
- Obtain pre-birth orders if possible to ensure immediate legal recognition.
- Complete all required post-birth legal steps, such as adoption or citizenship processes for international surrogacy.
Conclusion
Navigating parental rights in surrogacy requires careful legal planning to ensure that intended parents are recognized as the child’s legal guardians. Laws vary widely by location, making it essential to work with knowledgeable professionals and choose a jurisdiction with favorable regulations.